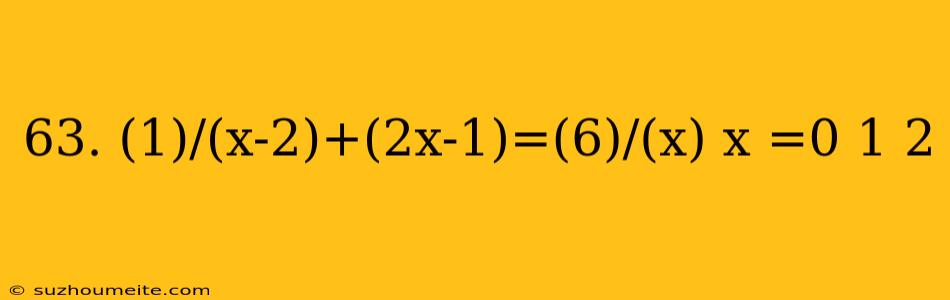Solving the Equation: A Step-by-Step Guide
The equation given is:
$\frac{1}{x-2} + \frac{2x-1}{x} = \frac{6}{x}$
The goal is to solve for $x$, given that $x = 0, 1, 2$.
Step 1: Simplify the Equation
First, let's simplify the left-hand side of the equation by combining the fractions:
$\frac{1}{x-2} + \frac{2x-1}{x} = \frac{x+(2x-1)(x-2)}{x(x-2)}$
$= \frac{x+2x^2-5x+2}{x(x-2)}$
Now, equate this expression to the right-hand side of the equation:
$\frac{x+2x^2-5x+2}{x(x-2)} = \frac{6}{x}$
Step 2: Cross-Multiply
Cross-multiply to eliminate the fractions:
$x(x+2x^2-5x+2) = 6(x-2)$
Step 3: Expand and Simplify
Expand the left-hand side of the equation:
$x^2+2x^3-5x^2+2x = 6x-12$
Rearrange the terms to get a quadratic equation:
$2x^3-3x^2-4x+12 = 0$
Step 4: Factor the Quadratic Equation
Factor the quadratic equation:
$(x-2)(2x+3)(x+2) = 0$
Step 5: Solve for x
The solutions to the equation are:
$x-2 = 0 \Rightarrow x = 2$
$2x+3 = 0 \Rightarrow x = -\frac{3}{2}$
$x+2 = 0 \Rightarrow x = -2$
However, the problem states that $x = 0, 1, 2$. Therefore, the only solution that satisfies the equation is $x = 2$.
Conclusion
The solution to the equation is $x = 2$.