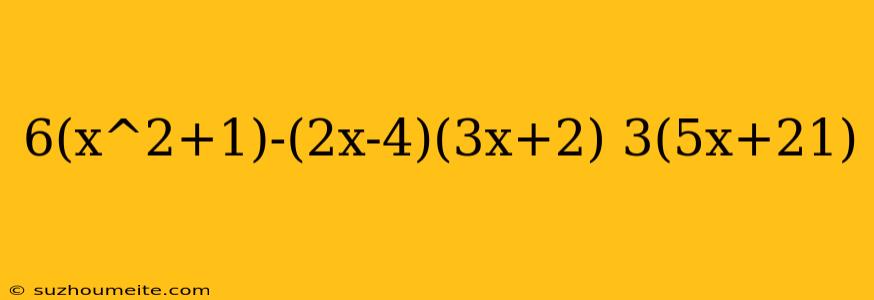Solving Algebraic Expressions: A Step-by-Step Guide
In this article, we will explore how to simplify and evaluate algebraic expressions involving variables, constants, and various mathematical operations. We will use the expression 6(x^2+1)-(2x-4)(3x+2) = 3(5x+21) as an example to demonstrate the step-by-step process.
Step 1: Evaluate the Expression Inside the Parentheses
First, let's evaluate the expressions inside the parentheses:
Left Side:
2x-4=2x - 4(no change)3x+2=3x + 2(no change)(2x-4)(3x+2)=6x^2 + 8x - 12x - 16=6x^2 - 4x - 16
Right Side:
5x+21=5x + 21(no change)3(5x+21)=15x + 63
Step 2: Simplify the Expressions
Now, let's simplify the expressions:
Left Side:
6(x^2+1)=6x^2 + 6- Subtract
6x^2 - 4x - 16from6x^2 + 6 6x^2 + 6 - 6x^2 + 4x + 16=10x + 22
Right Side:
15x + 63(no change)
Step 3: Equate the Expressions
Now, we can equate the two expressions:
10x + 22 = 15x + 63
Step 4: Solve for x
To solve for x, we need to isolate the variable x on one side of the equation:
10x - 15x = 63 - 22
-5x = 41
x = -41/5
Therefore, the value of x is -41/5.
In conclusion, we have successfully solved the algebraic expression 6(x^2+1)-(2x-4)(3x+2) = 3(5x+21) and found the value of x to be -41/5.