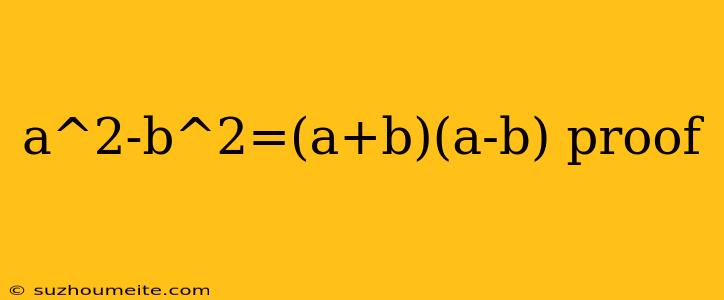Proof of the Difference of Squares Formula: a² - b² = (a + b)(a - b)
The difference of squares formula is a fundamental algebraic identity that states that the difference of the squares of two numbers is equal to the product of the sum and difference of those numbers. This formula can be proved using the distributive property of multiplication.
Proof:
-
Start with the right-hand side of the equation: (a + b)(a - b)
-
Apply the distributive property:
(a + b)(a - b) = a(a - b) + b(a - b)
-
Distribute again:
a(a - b) + b(a - b) = a² - ab + ba - b²
-
Simplify by combining the middle terms:
a² - ab + ba - b² = a² - b²
-
Therefore, we have shown that:
(a + b)(a - b) = a² - b²
Explanation:
The proof essentially shows that by expanding the product of the sum and difference of two numbers, we arrive at the difference of their squares. This demonstrates the equivalence of the two sides of the equation.
Applications:
The difference of squares formula has numerous applications in algebra and other fields, including:
- Factoring expressions: The formula can be used to factor expressions that contain a difference of squares.
- Simplifying algebraic expressions: The formula can be used to simplify complex expressions by replacing a difference of squares with its equivalent product.
- Solving equations: The formula can be used to solve equations involving a difference of squares.
Example:
Let's factor the expression x² - 9 using the difference of squares formula:
- Identify the squares: x² is the square of x, and 9 is the square of 3.
- Apply the formula: x² - 9 = (x + 3)(x - 3)
Therefore, we have factored the expression x² - 9 into the product of (x + 3) and (x - 3).