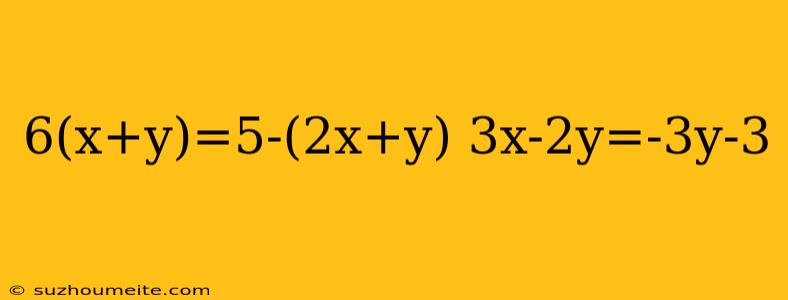Solving Linear Equations: 6(x+y) = 5 - (2x + y) and 3x - 2y = -3y - 3
In this article, we will learn how to solve a system of linear equations. We will focus on two equations: 6(x+y) = 5 - (2x + y) and 3x - 2y = -3y - 3.
Equation 1: 6(x+y) = 5 - (2x + y)
Let's start by simplifying the first equation:
6(x + y) = 5 - (2x + y)
Expanding the left side of the equation, we get:
6x + 6y = 5 - 2x - y
Now, let's rearrange the equation to have all the terms on one side:
6x + 6y + 2x + y = 5
Combine like terms:
8x + 7y = 5
Equation 2: 3x - 2y = -3y - 3
The second equation is already simplified, so we can move on to solving the system of equations.
Solving the System of Equations
We have two equations and two variables. We can solve this system using substitution or elimination. Let's use the elimination method.
First, we will multiply the two equations by necessary multiples such that the coefficients of y's in both equations are the same:
Equation 1: 8x + 7y = 5 Equation 2: 6(3x - 2y = -3y - 3) -> 18x - 12y = -18y - 18
Now, add both equations to eliminate the y variable:
(8x + 7y) + (18x - 12y) = 5 + (-18y - 18)
This simplifies to:
26x = -13
Now, divide by 26:
x = -13/26 x = -1/2
Now that we have the value of x, we can substitute it into one of the original equations to find the value of y. Let's use Equation 1:
8x + 7y = 5 8(-1/2) + 7y = 5
Solve for y:
7y = 5 + 4 7y = 9
Divide by 7:
y = 9/7
So, the solution to the system of equations is x = -1/2 and y = 9/7.
Conclusion
In this article, we solved a system of linear equations using the elimination method. We simplified the equations, multiplied them by necessary multiples, and added them to eliminate the y variable. Finally, we solved for x and y, finding the solution to be x = -1/2 and y = 9/7.