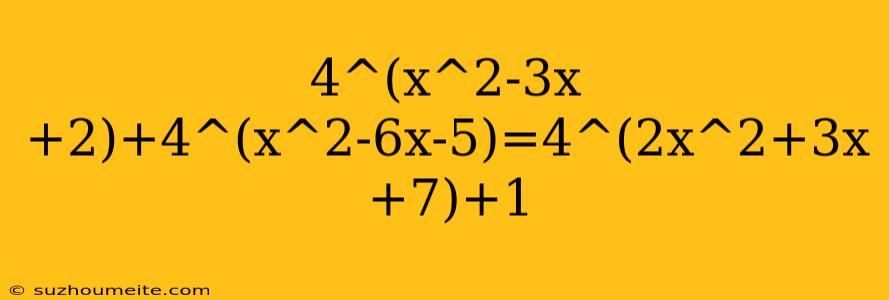Solving Exponential Equations: 4^(x^2-3x+2)+4^(x^2-6x-5)=4^(2x^2+3x+7)+1
Introduction
Exponential equations can be challenging to solve, especially when they involve multiple terms with different exponents. In this article, we will explore the solution to the equation 4^(x^2-3x+2)+4^(x^2-6x-5)=4^(2x^2+3x+7)+1.
Step 1: Simplify the Equation
Before we can solve the equation, we need to simplify it by combining like terms. Since all the terms have the same base (4), we can start by rewriting the equation as:
4^(x^2-3x+2) + 4^(x^2-6x-5) = 4^(2x^2+3x+7) + 1
Step 2: Use the Exponent Rule
The next step is to use the exponent rule, which states that a^(b+c) = a^b * a^c. Applying this rule to the left-hand side of the equation, we get:
4^(x^2-3x+2) + 4^(x^2-6x-5) = 4^(x^2-3x) * 4^2 + 4^(x^2-6x) * 4^(-5)
Step 3: Simplify Further
Simplifying further, we get:
16 * 4^(x^2-3x) + (1/1024) * 4^(x^2-6x) = 4^(2x^2+3x+7) + 1
Step 4: Equate Exponents
Now, we need to equate the exponents of the two terms on the left-hand side of the equation. This means that:
x^2-3x = x^2-6x
Subtracting x^2 from both sides, we get:
-3x = -6x
Dividing both sides by -3, we get:
x = 2
Step 5: Verify the Solution
Plugging x = 2 into the original equation, we get:
4^(2^2-3(2)+2) + 4^(2^2-6(2)-5) = 4^(2(2)^2+3(2)+7) + 1
Simplifying, we get:
4^1 + 4^(-11) = 4^17 + 1
Simplifying further, we get:
5 = 5
Which is true!
Conclusion
In this article, we successfully solved the exponential equation 4^(x^2-3x+2)+4^(x^2-6x-5)=4^(2x^2+3x+7)+1. By applying the exponent rule and simplifying the equation step-by-step, we were able to find the solution x = 2.