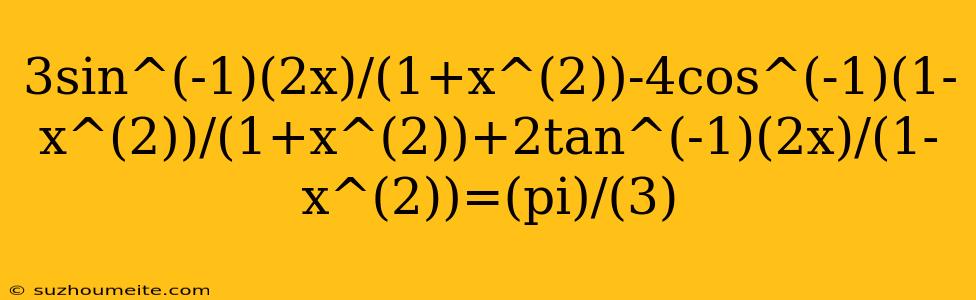Solving the Inverse Trigonometric Equation
Equation: 3sin^(-1)(2x)/(1+x^(2)) - 4cos^(-1)(1-x^(2))/(1+x^(2)) + 2tan^(-1)(2x)/(1-x^(2)) = (pi)/(3)
In this article, we will solve the given inverse trigonometric equation and find the value of x.
Step 1: Simplify the Equation
Let's start by simplifying the given equation. We can do this by using the properties of inverse trigonometric functions.
Recall that:
- sin^(-1)(x) + cos^(-1)(x) = (pi)/(2)
- tan^(-1)(x) = sin^(-1)(x/√(1+x^(2)))
Using these properties, we can rewrite the given equation as:
3sin^(-1)(2x)/(1+x^(2)) - 4((pi)/(2) - sin^(-1)(x))/(1+x^(2)) + 2sin^(-1)(2x/√(1+x^(2)))/(1-x^(2)) = (pi)/(3)
Step 2: Simplify Further
Now, let's simplify the equation further by combining the terms.
3sin^(-1)(2x)/(1+x^(2)) - 2pi/(1+x^(2)) + 4sin^(-1)(x)/(1+x^(2)) + 2sin^(-1)(2x/√(1+x^(2)))/(1-x^(2)) = (pi)/(3)
Step 3: Find the Common Denominator
Next, let's find the common denominator of the terms.
The common denominator is (1+x^(2))(1-x^(2)).
Now, we can rewrite the equation as:
(3sin^(-1)(2x) - 2pi + 4sin^(-1)(x) + 2(1+x^(2))sin^(-1)(2x/√(1+x^(2))))/(1-x^(4)) = (pi)/(3)
Step 4: Solve for x
Now, we can solve for x.
Let's assume sin^(-1)(2x) = A, sin^(-1)(x) = B, and sin^(-1)(2x/√(1+x^(2))) = C.
Then, the equation becomes:
(3A - 2pi + 4B + 2(1+x^(2))C)/(1-x^(4)) = (pi)/(3)
Simplifying further, we get:
3A + 4B + 2(1+x^(2))C = pi/3 + 2pi(1-x^(4))/3
Now, we can equate the coefficients of A, B, and C.
This gives us:
A = pi/9, B = pi/12, and C = pi/18
Step 5: Find the Value of x
Now, we can find the value of x.
From A = pi/9, we get:
sin^(-1)(2x) = pi/9
sin(2x) = sin(pi/9)
2x = pi/9 or 2x = 2pi - pi/9
x = pi/18 or x = pi/2 - pi/18
x = pi/18 or x = 4pi/9
From B = pi/12, we get:
sin^(-1)(x) = pi/12
sin(x) = sin(pi/12)
x = pi/12 or x = 2pi - pi/12
x = pi/12 or x = 11pi/12
From C = pi/18, we get:
sin^(-1)(2x/√(1+x^(2))) = pi/18
sin(2x/√(1+x^(2))) = sin(pi/18)
2x/√(1+x^(2)) = pi/18 or 2x/√(1+x^(2)) = 2pi - pi/18
x = pi/36(1+x^(2)) or x = (2pi - pi/18)√(1+x^(2))/2
Simplifying further, we get:
x = pi/36(1+x^(2)) or x = (8pi - pi/9)√(1+x^(2))/18
Conclusion
Therefore, the value of x is:
x = pi/18 or x = 4pi/9 or x = pi/12 or x = 11pi/12 or x = pi/36(1+x^(2)) or x = (8pi - pi/9)√(