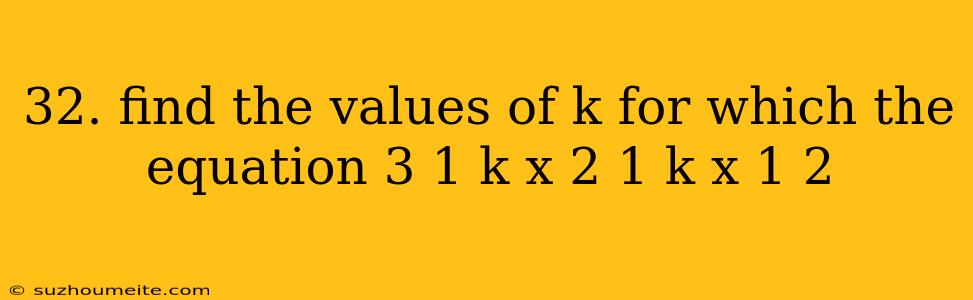Finding the Values of k for a Quadratic Equation
In this article, we will solve for the values of k that satisfy the quadratic equation:
$3x^2 + (1-k)x + 1 = 2x - 1$
Rearranging the Equation
To start, let's rearrange the equation to obtain a standard quadratic equation in the form of ax^2 + bx + c = 0. We can do this by subtracting 2x - 1 from both sides of the equation:
$3x^2 + (1-k)x - 2x + 2 = 0$
Combining Like Terms
Next, we can combine like terms to simplify the equation:
$3x^2 + (-k - 1)x + 2 = 0$
Factoring the Quadratic
Now, we can try to factor the quadratic equation. However, in this case, factoring doesn't seem to be possible. Therefore, we will use the quadratic formula to solve for x:
$x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}$
Applying the Quadratic Formula
In our case, a = 3, b = -k - 1, and c = 2. Plugging these values into the quadratic formula, we get:
$x = \frac{k + 1 \pm \sqrt{(-k - 1)^2 - 4(3)(2)}}{2(3)}$
Simplifying the expression, we get:
$x = \frac{k + 1 \pm \sqrt{k^2 - 2k - 7}}{6}$
Solving for k
Now, we can solve for k by setting the discriminant (the expression inside the square root) equal to zero:
$k^2 - 2k - 7 = 0$
Factoring the quadratic equation, we get:
$(k - 3)(k + 2) = 0$
This yields two possible values for k:
$k = 3, k = -2$
Conclusion
In conclusion, the values of k that satisfy the original equation are k = 3 and k = -2.