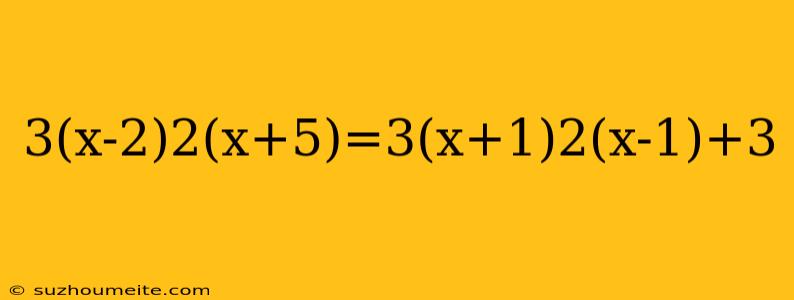Solving the Equation: 3(x-2)2(x+5)=3(x+1)2(x-1)+3
In this article, we will solve the equation 3(x-2)2(x+5)=3(x+1)2(x-1)+3. This equation involves quadratic expressions and requires some algebraic manipulations to arrive at the solution.
Expanding the Left-Hand Side
Let's start by expanding the left-hand side of the equation:
3(x-2)2(x+5) = 3(x-2)(x+5) (using the distributive property) = 3(x^2 + 3x - 10) (expanding the product) = 3x^2 + 9x - 30
Expanding the Right-Hand Side
Now, let's expand the right-hand side of the equation:
3(x+1)2(x-1)+3 = 3(x+1)(x-1) + 3 (using the distributive property) = 3(x^2 - 1) + 3 (expanding the product) = 3x^2 - 3 + 3 = 3x^2
Equating the Two Expressions
Now that we have expanded both sides of the equation, we can equate them:
3x^2 + 9x - 30 = 3x^2
Simplifying the Equation
Let's simplify the equation by combining like terms:
9x - 30 = 0
Solving for x
Finally, let's solve for x by adding 30 to both sides of the equation:
9x = 30 x = 30/9 x = 10/3
Therefore, the solution to the equation 3(x-2)2(x+5)=3(x+1)2(x-1)+3 is x = 10/3.
Conclusion
In this article, we have successfully solved the equation 3(x-2)2(x+5)=3(x+1)2(x-1)+3 by expanding both sides of the equation, equating them, and solving for x. The solution x = 10/3 is the result of our algebraic manipulations.