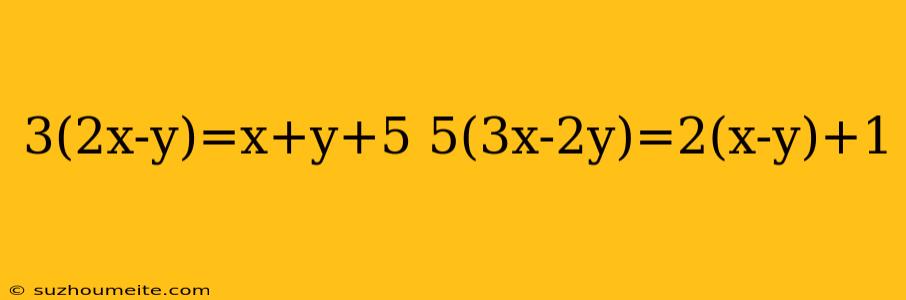Solving Systems of Linear Equations
In this article, we will explore how to solve a system of linear equations involving two variables. Specifically, we will look at the following system of equations:
Equation 1: 3(2x - y) = x + y + 5 Equation 2: 5(3x - 2y) = 2(x - y) + 1
To solve this system, we need to find the values of x and y that satisfy both equations.
Simplifying the Equations
Let's start by simplifying each equation:
Equation 1: 3(2x - y) = x + y + 5
Expanding the left-hand side, we get:
6x - 3y = x + y + 5
Rearranging the terms, we get:
5x - 4y = 5
Equation 2: 5(3x - 2y) = 2(x - y) + 1
Expanding the left-hand side, we get:
15x - 10y = 2x - 2y + 1
Rearranging the terms, we get:
13x - 8y = 1
Solving the System
Now that we have simplified the equations, we can solve the system using substitution or elimination methods. Here, we will use the elimination method.
Notice that if we multiply Equation 1 by 13 and Equation 2 by 5, we can eliminate the x-term:
Equation 1 (multiplied by 13): 65x - 52y = 65
Equation 2 (multiplied by 5): 65x - 40y = 5
Subtracting Equation 2 from Equation 1, we get:
-12y = 60
Dividing both sides by -12, we get:
y = -5
Now that we have found y, we can substitute this value into one of the original equations to find x. Let's use Equation 1:
5x - 4y = 5 5x - 4(-5) = 5 5x + 20 = 5 5x = -15 x = -3
Solution
Therefore, the solution to the system is x = -3 and y = -5.
Check
To verify our solution, we can plug the values of x and y back into both original equations:
Equation 1: 3(2(-3) - (-5)) = -3 + (-5) + 5 3(-6 + 5) = -3 3(-1) = -3 -3 = -3 (True)
Equation 2: 5(3(-3) - 2(-5)) = 2(-3 - (-5)) + 1 5(-9 + 10) = 2(-3 + 5) + 1 5(1) = 2(2) + 1 5 = 4 + 1 5 = 5 (True)
Our solution is correct!