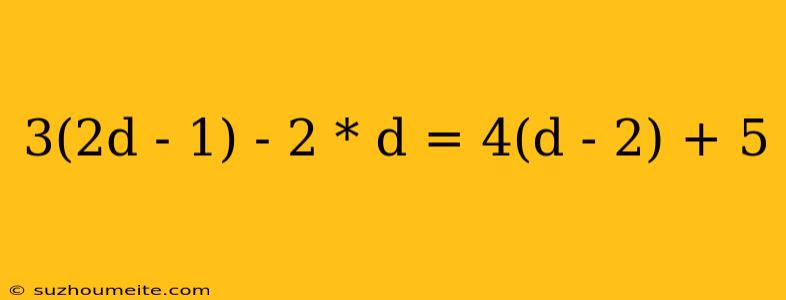Solving the Equation: 3(2d - 1) - 2d = 4(d - 2) + 5
In this article, we will solve the equation 3(2d - 1) - 2d = 4(d - 2) + 5. To solve this equation, we will start by simplifying both sides of the equation.
Simplifying the Left Side
The left side of the equation is 3(2d - 1) - 2d. To simplify this expression, we can start by evaluating the expression inside the parentheses.
3(2d - 1) = 6d - 3
Subtracting 2d from this expression, we get:
6d - 3 - 2d = 4d - 3
Simplifying the Right Side
The right side of the equation is 4(d - 2) + 5. To simplify this expression, we can start by evaluating the expression inside the parentheses.
4(d - 2) = 4d - 8
Adding 5 to this expression, we get:
4d - 8 + 5 = 4d - 3
Equating the Two Expressions
Now that we have simplified both sides of the equation, we can equate them:
4d - 3 = 4d - 3
Solution
As we can see, the equation is an identity, meaning that it is true for all values of d. Therefore, there is no specific solution to the equation.
In conclusion, we have solved the equation 3(2d - 1) - 2d = 4(d - 2) + 5 and found that it is an identity.