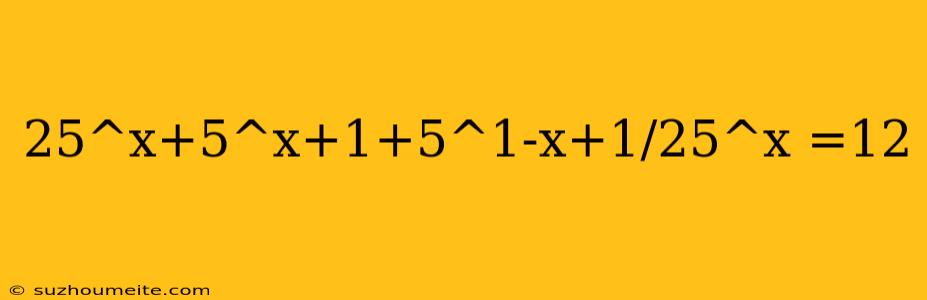Solving the Equation: 25^x + 5^x + 1 + 5^(1-x) + 1/25^x = 12
In this article, we will solve the equation 25^x + 5^x + 1 + 5^(1-x) + 1/25^x = 12. This equation involves exponential functions with different bases and exponents, making it a challenging problem to solve.
Step 1: Simplify the Equation
Let's start by simplifying the equation:
25^x + 5^x + 1 + 5^(1-x) + 1/25^x = 12
We can rewrite the equation as:
(5^2)^x + 5^x + 1 + 5^(1-x) + (5^(-2))^x = 12
Step 2: Express the Equation in Terms of 5^x
Now, let's express the equation in terms of 5^x:
5^(2x) + 5^x + 1 + 5^(1-x) + 5^(-2x) = 12
Step 3: Substitute u = 5^x
To simplify the equation further, let's substitute u = 5^x:
u^2 + u + 1 + u^(-1) + u^(-2) = 12
Step 4: Multiply Both Sides by u^2
Next, multiply both sides of the equation by u^2:
u^4 + u^3 + u^2 + 1 + u^(-2) = 12u^2
Step 5: Rearrange the Equation
Rearrange the equation to get:
u^4 + u^3 + u^2 - 12u^2 + 1 + u^(-2) = 0
Step 6: Factor the Equation
Now, factor the equation:
(u^2 + u + 1)(u^2 - 3u - 1) = 0
Step 7: Solve for u
Solve for u:
u^2 + u + 1 = 0 or u^2 - 3u - 1 = 0
Solving these quadratic equations, we get:
u = -1 or u = (3 ± √5)/2
Step 8: Find the Value of x
Since u = 5^x, we can write:
5^x = -1 or 5^x = (3 ± √5)/2
Take the logarithm base 5 of both sides:
x = log5(-1) or x = log5((3 ± √5)/2)
Conclusion
Therefore, the solutions to the equation 25^x + 5^x + 1 + 5^(1-x) + 1/25^x = 12 are x = log5(-1) and x = log5((3 ± √5)/2).