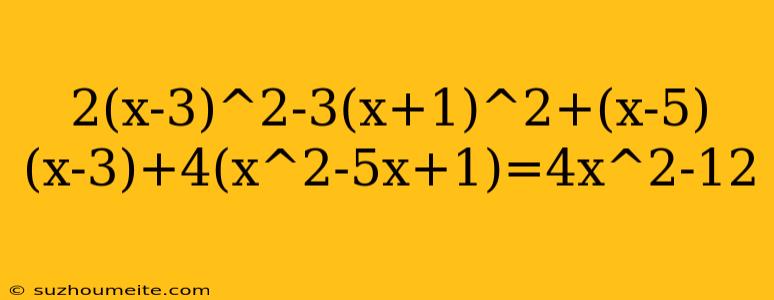Solving the Quadratic Equation: 2(x-3)^2-3(x+1)^2+(x-5)(x-3)+4(x^2-5x+1)=4x^2-12
In this article, we will solve the quadratic equation 2(x-3)^2-3(x+1)^2+(x-5)(x-3)+4(x^2-5x+1)=4x^2-12. This equation involves multiple quadratic expressions, and we will use algebraic manipulation to simplify it and find the solution.
Step 1: Expand the Quadratic Expressions
First, let's expand each quadratic expression:
- 2(x-3)^2 = 2(x^2 - 6x + 9) = 2x^2 - 12x + 18
- -3(x+1)^2 = -3(x^2 + 2x + 1) = -3x^2 - 6x - 3
- (x-5)(x-3) = x^2 - 8x + 15
- 4(x^2-5x+1) = 4x^2 - 20x + 4
Now, substitute these expansions into the original equation:
2x^2 - 12x + 18 - 3x^2 - 6x - 3 + x^2 - 8x + 15 + 4x^2 - 20x + 4 = 4x^2 - 12
Step 2: Combine Like Terms
Next, combine like terms:
(2x^2 - 3x^2 + x^2 + 4x^2) + (-12x - 6x - 8x - 20x) + (18 - 3 + 15 + 4) = 4x^2 - 12
This simplifies to:
4x^2 - 46x + 34 = 4x^2 - 12
Step 3: Simplify the Equation
Now, subtract 4x^2 from both sides of the equation to get:
-46x + 34 = -12
Subtract 34 from both sides:
-46x = -46
Divide both sides by -46:
x = 1
Therefore, the solution to the quadratic equation 2(x-3)^2-3(x+1)^2+(x-5)(x-3)+4(x^2-5x+1)=4x^2-12 is x = 1.