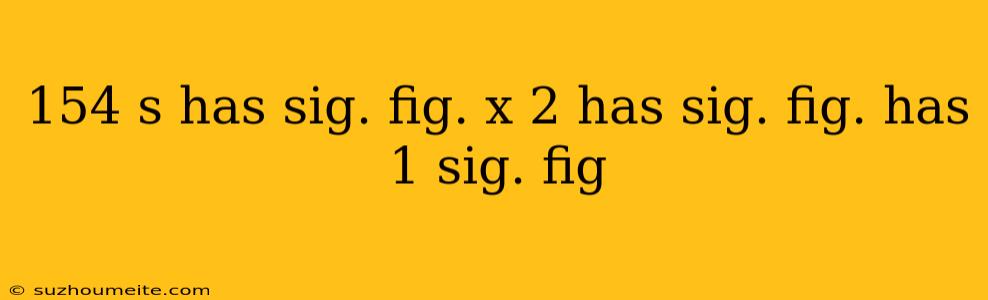Significant Figures in Multiplication and Division
When performing multiplication and division operations, it's essential to understand how to handle significant figures (sig. fig.). Significant figures represent the number of digits in a value that are known to be reliable and accurate. In this article, we'll explore how to handle significant figures in multiplication and division operations.
Rule for Multiplication and Division
When multiplying or dividing two or more numbers, the result should have the same number of significant figures as the number with the fewest significant figures. This rule ensures that the result is no more precise than the least precise number in the operation.
Example 1: Multiplication
Consider the multiplication operation: 154 (3 sig. fig.) × 2 (1 sig. fig.)
To determine the number of significant figures in the result, we look at the number with the fewest significant figures, which is 2 with 1 sig. fig. Therefore, the result should have 1 sig. fig.
Result: approximately 300 (1 sig. fig.)
Why is this important?
Understanding significant figures is crucial in scientific calculations because it helps to avoid reporting false precision. For instance, if we reported the result of the above multiplication as 308, we would be implying that we know the value with more precision than we actually do. By following the rule for significant figures, we ensure that our results are reliable and accurate.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when performing multiplication and division operations, it's essential to consider the number of significant figures in each number. The result should have the same number of significant figures as the number with the fewest significant figures. By following this rule, we can ensure that our calculations are accurate and reliable.