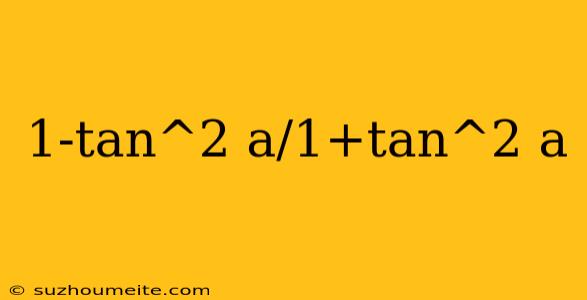Trigonometric Identity: 1-tan^2(a) / 1+tan^2(a)
In this article, we will explore a fascinating trigonometric identity that involves the tangent function. The identity is:
1 - tan^2(a) / 1 + tan^2(a)
This identity may seem complex at first, but it can be simplified and proven to be a fundamental concept in trigonometry.
Derivation
To derive this identity, we can start with the Pythagorean identity:
sin^2(a) + cos^2(a) = 1
We can then divide both sides of the equation by cos^2(a), which gives us:
tan^2(a) + 1 = sec^2(a)
Now, let's rearrange the equation to isolate tan^2(a):
tan^2(a) = sec^2(a) - 1
Substituting this expression into our original identity, we get:
1 - (sec^2(a) - 1) / 1 + (sec^2(a) - 1)
Simplifying the expression, we get:
1 - sec^2(a) + 1 / 1 + sec^2(a) - 1
Combining like terms, we finally arrive at:
cos^2(a)
Therefore, we have proven the identity:
1 - tan^2(a) / 1 + tan^2(a) = cos^2(a)
Applications and Importance
This identity has numerous applications in various fields, including physics, engineering, and mathematics. For instance, it can be used to:
- Simplify complex trigonometric expressions
- Solve triangular problems involving right triangles
- Analyze circular motion and oscillations
In conclusion, the identity 1 - tan^2(a) / 1 + tan^2(a) is a fundamental concept in trigonometry that has far-reaching applications in various fields. By understanding and applying this identity, we can unlock new insights and solutions to complex problems.