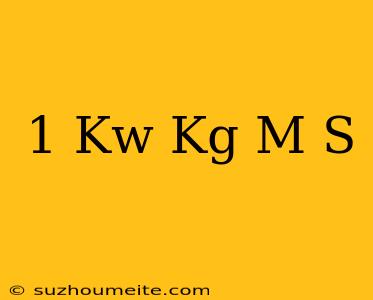1 kW = kg m/s: Understanding the Fascinating World of Energy and Power
In the realm of physics, there exists a fascinating relationship between energy and power. One kilowatt (1 kW) is equivalent to a mass of 1 kilogram being moved at a velocity of 1 meter per second (kg m/s). This intriguing equation has far-reaching implications in various fields, from engineering to astronomy. In this article, we'll delve into the world of energy and power, exploring the significance of 1 kW = kg m/s.
Energy and Power: The Basics
Before we dive into the equation, let's briefly explore the fundamental concepts of energy and power.
Energy is the capacity to do work, measured in joules (J). It's the total amount of work an object can perform. Think of it as the fuel in your car's tank.
Power, on the other hand, is the rate at which energy is transferred or converted, measured in watts (W). It's the rate at which your car's engine burns fuel.
The Equation: 1 kW = kg m/s
Now, let's break down the equation:
1 kW = 1 kg × 1 m/s
What does this mean? Essentially, it means that 1 kilowatt of power is equivalent to accelerating a mass of 1 kilogram to a velocity of 1 meter per second. To put it simply, if you were to push a 1 kg object at a speed of 1 m/s, you'd be expending 1 kW of power.
Real-World Applications
This equation has significant implications in various fields:
- Engineering: In mechanical engineering, understanding the relationship between power and energy is crucial for designing efficient engines, gears, and transmission systems.
- Aerospace: When launching satellites or spacecraft, precise calculations of energy and power are necessary to ensure a successful mission.
- Sports: In athletic events like sprinting, understanding the relationship between power and speed can help athletes optimize their performance.
Conclusion
The equation 1 kW = kg m/s may seem simple, but it holds significant importance in understanding the intricate dance between energy and power. By grasping this fundamental concept, we can unlock more efficient designs, more precise calculations, and a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of the universe.
Remember:
- Energy is the total capacity to do work (measured in joules, J)
- Power is the rate at which energy is transferred (measured in watts, W)
- 1 kW = 1 kg × 1 m/s (the intriguing equation that binds energy and power)