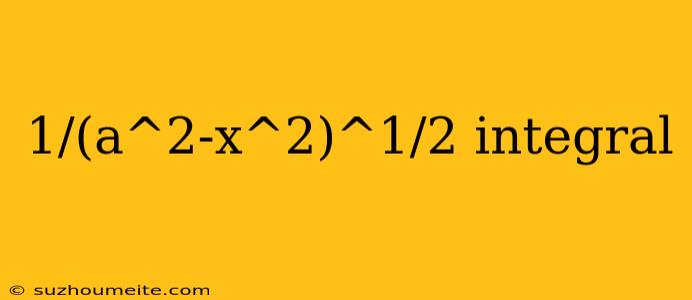Integral of 1/(a^2-x^2)^1/2
The integral of 1/(a^2-x^2)^1/2 is a classic example of a trigonometric substitution problem. In this article, we will explore the steps to evaluate this integral.
The Problem
The given integral is:
$\int \frac{1}{\sqrt{a^2-x^2}} dx$
Trigonometric Substitution
The key to evaluating this integral is to use the trigonometric substitution:
$x = a \sin(u)$
This substitution will allow us to rewrite the integral in terms of the variable $u$.
Rewriting the Integral
Using the substitution, we get:
$dx = a \cos(u) du$
Substituting this into the original integral, we get:
$\int \frac{1}{\sqrt{a^2-x^2}} dx = \int \frac{1}{\sqrt{a^2 - a^2 \sin^2(u)}} a \cos(u) du$
Simplifying the expression under the radical, we get:
$\sqrt{a^2 - a^2 \sin^2(u)} = \sqrt{a^2 \cos^2(u)} = a \cos(u)$
So, the integral becomes:
$\int \frac{1}{a \cos(u)} a \cos(u) du$
Evaluating the Integral
The integral simplifies to:
$\int 1 du = u + C$
Back-Substitution
Now, we need to substitute back in terms of the original variable $x$. We know that:
$x = a \sin(u)$
So, we get:
$u = \sin^{-1}(\frac{x}{a})$
Substituting this back into the result, we get:
$\int \frac{1}{\sqrt{a^2-x^2}} dx = \sin^{-1}(\frac{x}{a}) + C$
Conclusion
In this article, we have seen how to evaluate the integral of 1/(a^2-x^2)^1/2 using a trigonometric substitution. The final result is an inverse sine function.